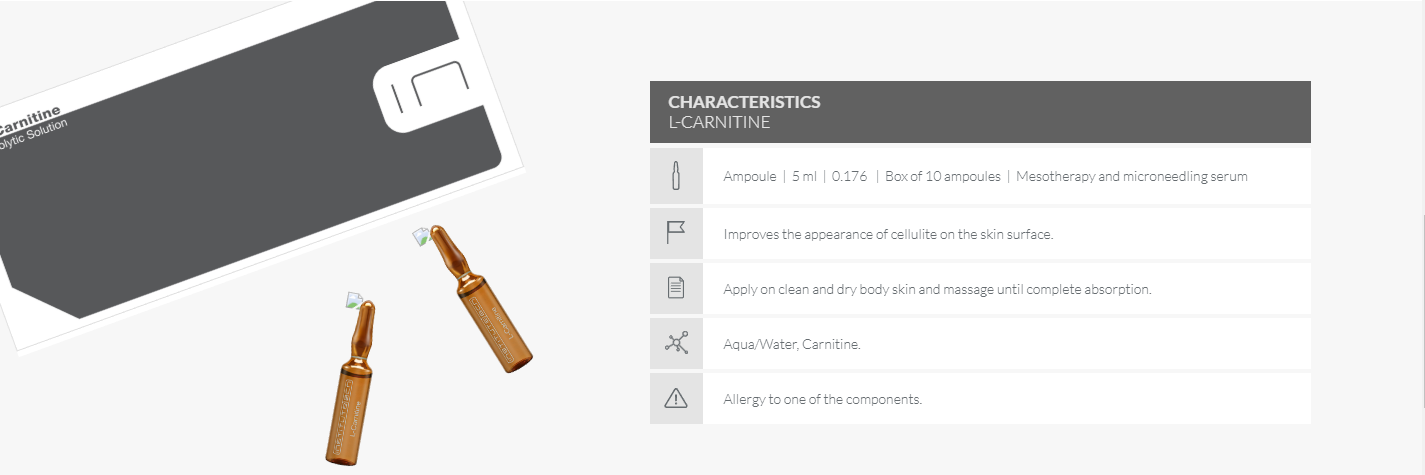
LIPOLYTIC SOLUTION
L-Carnitine exists naturally in the body and is an essential cofactor of acid metabolism of lipids. The best known function of carnitine is its essential role in transporting longchain fatty acids into mitochondria for boxidation, thus being of fundamental importance in lipid catabolism and energy production.
Besides this main action, carnitine has other physiological roles, namely detoxification of non metabolizable acyl residues, general buffering of the acylCoA to CoA ratio, and the shuttling of the acyl groups of acylCoAs, such as peroxisomes, cytosol and mitochondria. All these functions are mediated by a group of carnitine acyltransferases, enzymes specific for the acyl- chain lenghts.
According to some authors, carnitine and its esters protect cells from oxidative damage both by inhibiting free radical propagation and by contributing to repair the oxidized membrane phospholipids. Since the fat burning is such a major source of muscular energy, deficiencies in L-Carnitine are manifested as low energy levels and muscular weakness.br />
On the basis of the multiple functions described above, carnitine represents a precious aid in the treatment of cellulitis, condition where an alteration of the microcirculation affects the normal functionality of adipocytes, which start to synthesize and accumulate excessive amounts of triglycerides.
The action of carnitine is particularly valuable since it not only promotes lipid catabolism, but also helps in detoxifying and regenerating cells, restoring the physiological functionality of the dermis.
|